Vanadium(V) chloride
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
vanadium pentachloride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| Cl10V2 | |
| Molar mass | 456.38 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | black solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
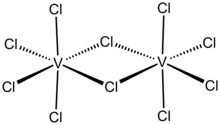
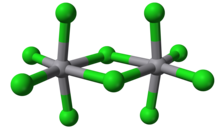
Vanadium(V) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula VCl5. It is a black diamagnetic solid. The molecules adopt a bioctahedral structure similar to that of niobium(V) chloride.[1]
Preparation and reactions
Vanadium(V) chloride is prepared from the vanadium pentafluoride with excess boron trichloride:
- 2 VF5 + 10 BCl3 → [VCl5]2 + 10 BF2Cl
It is unstable at room temperature with respect to vanadium(IV) chloride:
- [VCl5]2 → 2 VCl4 + Cl2
In contrast, the heavier analogues NbCl5 and TaCl5 are stable and not particularly oxidizing.
References
- ^ Tamadon, Farhad; Seppelt, K. (2012). "The Elusive Halides VCl5, MoCl6, and ReCl6". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 52 (2): 767–769. doi:10.1002/anie.201207552. PMID 23172658.
